DiabeticLink
Project Summary: DiabeticLink
Today’s healthcare has become cost-prohibitive for many and suffers substantially from medical errors and waste (National Research Council, 2009). Anderson & Markovich (2009) reported that the U.S. spends $1.7 trillion annually (16% of GDP) on healthcare, yet produces significantly lower health outcomes than many other developed countries. Many new government initiatives exist to address these continuing problems and improve healthcare-related outcomes. For example, as part of the 2009 federal stimulus package, the HITECH Act for healthcare information technology (IT) stipulates that healthcare entities in the U.S. need to use IT to fix ingrained problems, with $19 billion in 2011 and a total of $50 billion allocated to this effort over the next 5 years. In January 2009, China’s government announced a plan to spend more than $120 billion on the first phase of a 10-year overhaul of its healthcare system (Fairclough, 2009). In academia there has also been significant recent interest in adopting and advancing IT for effective healthcare. The 2009 National Research Council report on “Computational Technology for Effective Health Care” suggests an overarching grand research challenge of developing “patient-centered cognitive support.” This report also points out several IT-centric research challenges, including: virtual patient modeling, healthcare automation, healthcare data sharing and collaboration, and healthcare data management at scale. A major research goal of these programs is to develop trusted healthcare systems that provide relevant decision support to clinicians and patients, and offer “just in time, just for me” advice at the point of care.
In a research commentary article by Wactlar, Pavel and Barkis, entitled “Can Computer Science Save Healthcare?” (Wactlar, et al., 2011) the authors discuss ways that computer science, or more generally, IT research could help to resolve some of the healthcare crises in America. They proposed a program of research and development along four technology thrusts to enable this vision: (1) creating an interoperable, digital infrastructure of universal health data and knowledge, (2) utilizing diverse data to provide automated and augmented insight, discovery, and evidence-based health and wellness decision support, (3) a cyber-based empowering of patients and healthy individuals to play a substantial role in their own health and treatment, and (4) monitoring and assisting individuals with intelligent systems: sensors, devices and robotics, to maintain function and independence.
Thrust areas 2 and 3, healthcare decision support and cyber-enabled patient empowerment, are of particular relevance to our research. Given the growing numbers of electronic health records, results of clinical trials, high-throughput genomic research findings, the biomedical research literature, and even health-related social data, healthcare is entering the realm of “Health Big Data.” Advanced data mining, machine learning, natural language processing, and data visualization research, carefully developed with clinical consideration in the diagnosis, treatment, and patient care cycle, are critically needed. Moreover, patients and their families are and should be full healthcare decision partners. Patients who actively participate in their healthcare have better outcomes and a perceived quality of life that is better than those who do not (Bandura, 2007). Patient empowerment can be supported by new communication and sensor technologies, decision support systems, and health social media tools.
In light of the emerging Health 2.0 opportunities, our project focuses on health big data research relating to health social media content management and analytics, patient community portal development, mobile and cloud-based health app delivery, and patient community support assessment. We developed advanced social media analytics techniques and tools for patient community networks, symptom-disease-treatment associations, health community question-answering, and patient portal system support. These techniques and tools have been developed and evaluated for diabetes, the seventh leading cause of death in the U.S. Our technical research was guided and assessed by seasoned endocrinologists and health clinicians in our highly inter-disciplinary team. We also conducted several field studies assessing the usability and value of our proposed diabetic patient support portal for selected diabetic patient groups.
Research Objectives
Our excellent and experienced research team was composed of accomplished computer/information scientists, nutritional scientist, and medical professionals. Leveraging our data, text, and web mining experience and extensive healthcare knowledge, we took a data-centric and patient-centered approach in developing algorithms and techniques to support cyber-enabled patient empowerment, and personalized healthcare and community mapping. The specific research objectives of this highly integrative project include:
- Cyber-enabled Patient Empowerment
- Develop text processing techniques to extract symptom-disease-treatment information embedded in health social media sites.
- Develop sentiment analysis techniques suitable for extracting the emotional responses associated with health-related social media content.
- Develop evolutionary topic detection techniques for patient community question-answering.
- Personalized Healthcare and Community Mapping
- Develop computational techniques to identify participant interaction networks in social media sites.
- Develop community mapping and visualization techniques for health social media contents.
- Develop a diabetes patient portal system, DiabeticLink, for finding similar patients and mapping the patient community.
- Assessment and Evaluation
- Perform technology assessment on the proposed data mining, text mining, and visualization techniques.
- Develop a cloud-based mobile app to access DiabeticLink patient portal system and perform multi-stage patient-group field evaluation studies.
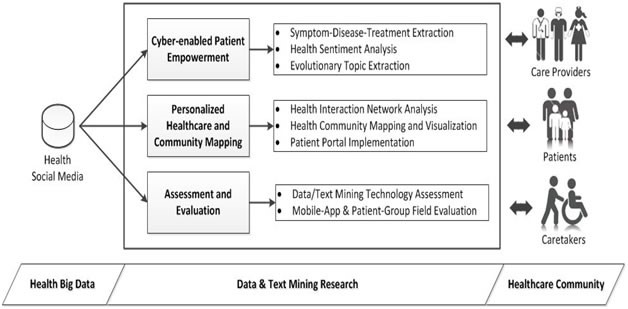
Research Framework: Patient-Centric Healthcare Decision Support
Our research plan encompassed three areas: cyber-enabled patient empowerment, personalized healthcare and community mapping, and assessment and evaluation. Our research framework is shown below.
Results
DiabeticLink is an intelligent diabetes self-management website that provides a one-stop solution for all diabetes related issues. The website provides content mashup (news, videos, blogs) from credible diabetes related websites, a unique risk engine to predict risk of hospitalization in diabetics, online tracking and enhanced visualization of tracked data and a community feature where people with similar issues can connect. This system is aimed at improving health outcomes among diabetics.
Funding
Subcontract from Caduceus Intelligence Corporation, "STTR Phase I: The Development and Evaluation of an Intelligent Diabetes Self-Management Tool," $85,354 (From NSF award IIP-1417181 to Caduceus Intelligence Corporation), June 3, 2014 - June 30, 2015.